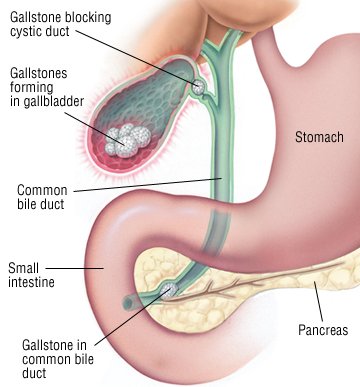
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just beneath your liver. The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid called bile that's released into your small intestine.
Gallstones range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Some people develop just one gallstone, while others develop many gallstones at the same time.
Gallstones are common in the United States. People who experience symptoms from their gallstones usually require gallbladder removal surgery. Gallstones that don't cause any signs and symptoms typically don't need treatment.
Causes- It is not clear what causes gallstones to form. Doctors think gallstones may result when:
· Your bile contains too much cholesterol. Normally, your bile contains enough chemicals to dissolve the cholesterol excreted by your liver. But if your liver excretes more cholesterol than your bile can dissolve, the excess cholesterol may form into crystals and eventually into stones.
· Your bile contains too much bilirubin. Bilirubin is a chemical that's produced when your body breaks down red blood cells. Certain conditions cause your liver to make too much bilirubin, including liver cirrhosis, biliary tract infections and certain blood disorders. The excess bilirubin contributes to gallstone formation.
· Your gallbladder doesn't empty correctly. If your gallbladder doesn't empty completely or often enough, bile may become very concentrated and this contributes to the formation of gallstones.
Types of gallstones
Types of gallstones that can form in the gallbladder include:
· Cholesterol gallstones. The most common type of gallstone, called a cholesterol gallstone, often appears yellow in color. These gallstones are composed mainly of undissolved cholesterol, but may contain other components.
· Pigment gallstones. These dark brown or black stones form when your bile contains too much bilirubin
Symptoms-- Gallstones may cause no signs or symptoms. If a gallstone lodges in a duct and causes a blockage, the resulting signs and symptoms may include:
· Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the upper right portion of your abdomen
· Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the center of your abdomen, just below your breastbone
· Back pain between your shoulder blades
· Pain in your right shoulder
· Nausea or vomiting
Gallstone pain may last several minutes to a few hours
Risk factors--Factors that may increase your risk of gallstones include:
· Being female
· Being age 40 or older
· Being a Native American
· Being a Mexican-American
· Being overweight or obese
· Being sedentary
· Being pregnant
· Eating a high-fat diet
· Eating a high-cholesterol diet
· Eating a low-fiber diet
· Having a family history of gallstones
· Having diabetes
· Losing weight very quickly
· Taking medications that contain estrogen, such as oral contraceptives or hormone therapy drugs
· Having liver disease
Complications-Complications of gallstones may include:
Inflammation of the gallbladder. A gallstone that becomes lodged in the neck of the gallbladder can cause inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis). Cholecystitis can cause severe pain and fever.
Blockage of the common bile duct. Gallstones can block the tubes (ducts) through which bile flows from your gallbladder or liver to your small intestine. Jaundice and bile duct infection can result.
Blockage of the pancreatic duct. The pancreatic duct is a tube that runs from the pancreas to the common bile duct. Pancreatic juices, which aid in digestion, flow through the pancreatic duct.
A gallstone can cause a blockage in the pancreatic duct, which can lead to inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis). Pancreatitis causes intense, constant abdominal pain and usually requires hospitalization.
Gallbladder cancer. People with a history of gallstones have an increased risk of gallbladder cancer. But gallbladder cancer is very rare, so even though the risk of cancer is elevated, the likelihood of gallbladder cancer is still very small.
HOMOEOPATHIC REMEDIES
Homoeopathic remedies are very effective for the treatment of gall stones. Homoeopathic medicines not only dissolves the stones but also prevent the further formation of stones. Some of the important remedies are given below-
BERBERIS VULGARIS Q- Berberis Vulgaris is an excellent remedy for gall stone colic and also for the removal of stones. It is of great help for treating sharp, stitching pains in the gall bladder. The pain may get worse from applying pressure.
BELLADONNA 30- Belladonna is very effective for acute gall stone colic. It can be repeated often till the pain disappears.
CHINA 30—China is another excellent remedy for acute pain in gall bladder when abdomen is bloated with excess of gas.The whole abdomen is full of gas with a painful distension. Walking may providea slight relief from distension. Here the pain is more at night. Vomiting of undigested food may occur.
CARBO VEG 30- Carbo veg is very effective for gas in abdomen in patients suffering from gall stone.Carbo veg is prescribed when the gas is present mainly in the upper region of abdomen. The abdomen is heavy, tenseand distended. Passage of a little gas providesa slight relief from distension.
CRDUS MARIANUS Q—Cardus mar. is an excellent for gall stone colic. There is swelling of the gall bladder with tenderness and pain. Cradus mar. prevents further formation of gall stone.
CHELIDINIUM MAJ. 200—Cheledonium is an excellent remedy for gall stone colic and also for the prevention of gall stone formation. Chelidinum is very effective for gall stone and jaundice due to obstruction of gall bladder by gall stones. Here the pain is below the right shoulder in the scapulae.Chelidonium helps for the expulsion of gall stones if already formed.
COLOCYNTH 30-Colocynth is the ideal remedy when the gall stone pain is of a cutting, shooting nature and getting better by bending double or applying pressure.
CHOLESTERINUM 3X-Cholesterinum is considered a specific remedy for gall stones. It relieves the pain at once.
CHIONANTHUS Q- Chionanthus is considered a prominent remedy for prevention of formation of gall stones. It helps expulsion of gall stones if already formed.
FEL TAURI 2X—Feltauri is an excellent remedy for gall stones. This medicine increases the duodenal secretion , emulsifies fat and increases the action of intestines. Liquefies bile and removes the obstruction of gall ducts. Feltauri helps the expulsion of biliary calculi.
HYDRASTIS CAN 30- Hydrastis is prescribed when gall stone with dragging in the right groin and right testicle. Here jaundice and constipation present.
ARSENICUM ALBUM AND IPECAC 30- Nausea and vomiting usually occur along with the colic due to gall stones or when the gall bladder gets inflamed. Natural Homeopathic medicine Arsenic Album is very beneficial when the vomiting occurs immediately after eating or drinking anything. Burning type of pains in abdomen usually accompany. Homeopathic medicine Ipecac gives very good results when there is persistent nausea and vomiting.
LYCOPODIUM CLAVATUM 200-Lycopodium is a very effective Homeopathic medicine for gas in abdomen in patients suffering from gall stones.There is excess gas in abdomen , especially the lower region. The abdomen is bloated even after light eating. Mainly starchy food and flatulent food like cabbage worsenthe problem.Patient desires warm food and likes sweets.
MERCURIUS IOD. 30-Merc .iodide is prescribed when a lump on the bladder with enlargement of the liver is present. Here the urine smells like mustard oil. The patient experiences great pain.
NUX VOMICA 30-Nux vomica is an excellent remedy for acidity due to gall stones.
Nux Vomica is prescribed for patients complaining of acidity after eating. Such patients complain of sour burps, nausea and weight in stomach after eating. When the intake of coffee, spicy food or alcoholic drinks raises the dyspeptic symptoms, Nux Vomica yields excellent results.
RAPHANUS 30- Raphanus can be used with much efficiency for treating excessive gas in abdomen after removal of gall bladder. The gas neither moves upwards or downwards, resulting in a bloated abdomen
PULSATILLA 30- Pulsatilla is the top remedy for gallstones when eating of excessive fried or fatty food like butter or cream leads to acidity.
SOME MOTHER TINCTURE FOR GALL STONE COLIC
ATISTA INDICA Q- Colic pain around the umbilicus which makes the patient senseless. Pain aggravates after eating and is relieved by passing flatus. Nausea aggravates in morning. Canine hunger and desire for sweets.Indigestion from fried things. Bitter taste in the mouth.Vomiting after taking milk
further formation of gall stones
DIOSCOREA Q- Severe pain.Pain ameliorates on bending backward
CACTUS GRANDIFLORUS Q- Gall stones with constriction and cardiac affections
STIGMATA MADAGUS Q- Relives at once the violent pain if given during paroxysm
TERMINALIA CHEBULA Q- Intense pain in abdomen aggravated at night. Pain aggravated by sitting, better by lying down. Flatulence and distension of abdomen relieved by passing flatus.Anorexia , profuse salivation and bitter taste n mouth. Tongue is coated brown.
PREVENTION- :Diet may play a role in gallstones.---Fats. Although fats (particularly saturated fats found in meats, butter, and other animal products) have been associated with gallstone attacks, Fiber. High intake of fiber has been associated with a lower risk for gallstones. Nuts. Studies suggest that people may be able to reduce their risk of gallstones by eating more nuts (peanuts and tree nuts, such as walnuts and almonds).
Fruits and Vegetables. had the lowest risk of developing symptomatic gallstones that required removal of the gallbladder.
Lecithin. Lecithin is a key component of bile. It contains choline and inositol, two compounds that are important for the breakdown of fat and cholesterol. Low levels of lecithin may precipitate the formation of cholesterol gallstones. Dietary lecithin is available in health food stores and is found in eggs, soybeans, liver, wheat germ, and peanuts. There is no evidence, however, that lecithin supplements or foods containing it can prevent gallstones in humans.
Sugar. High-intake of sugar has been associated with an increased risk for gallstones.
Alcohol. A few studies have reported a lower risk for gallstones with alcohol consumption. Preventing Gallstones during Weight Loss Maintaining a normal weight and avoiding rapid weight loss are the keys to reducing the risk of gallstones
Email-plantmedicines@yahoo.com
No comments:
Post a Comment